The physical theoretical basis of the measurement principle of the Coriolis Mass Flowmeter was proposed by the French physicist Mr. Coriolis 200 years ago, which can be directly detected by mass flow.
 | The Coriolis flowmeter has a measurement tube inside, and the excitation coil ensures that the measurement tube is always vibrating. If there is no fluid flow within the measurement tube, the measurement tube will be uniformly vibrated; the phase sensors are located in the inlet and outlet of the fluid, and record the vibration. When the fluid in the measuring tube begins to flow, the measurement tube vibration is distorted due to the action of fluid inertia. |
 | Due to the Coriolie effect, the inlet of the pipeline and the exit portion vibrate in different directions at the same time. The extremely sensitive sensor acquires the change in the pipe vibration in time and space, by recording "phase difference", can be directly calculate out the mass of the liquid or gas. The faster the flow rate, the larger the flow rate, and larger the shift of the measurement tube vibration. |
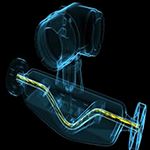 | The application of Corioli's measurement principle is more and it can also measure the density of the fluid, and the sensor needs to record the vibration frequency, that is, the number of times the measurement tube is vibrated within one second. For example, honey has a larger density than water, so the measuring tube that is full of water is more frequent than the measurement tube filled with honey, so the vibration frequency can directly reflect the density of the liquid, and the vibration of the tube can simultaneously detect the flow and density, and they are independent of each other; so it can measure multiple process variables by Coriolis Mass Flowmeter, such as mass flow, volume flow, density, temperature, even viscosity. |
Previous: No Information